Plan-and-Execute¶
This notebook shows how to create a "plan-and-execute" style agent. This is heavily inspired by the Plan-and-Solve paper as well as the Baby-AGI project.
The core idea is to first come up with a multi-step plan, and then go through that plan one item at a time. After accomplishing a particular task, you can then revisit the plan and modify as appropriate.
The general computational graph looks like the following:
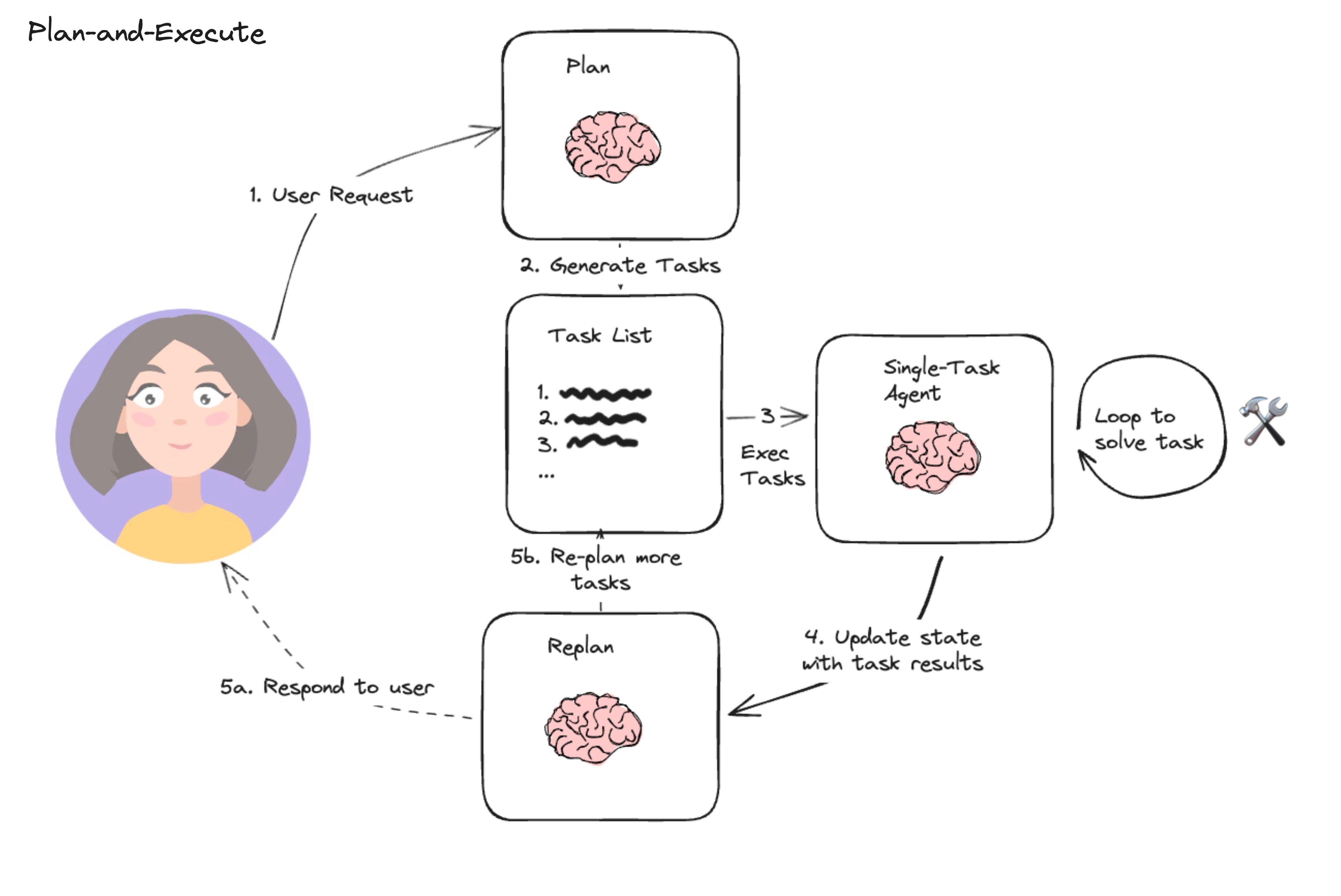
This compares to a typical ReAct style agent where you think one step at a time. The advantages of this "plan-and-execute" style agent are:
- Explicit long term planning (which even really strong LLMs can struggle with)
- Ability to use smaller/weaker models for the execution step, only using larger/better models for the planning step
The following walkthrough demonstrates how to do so in LangGraph. The resulting agent will leave a trace like the following example: (link).
Setup¶
First, we need to install the packages required.
%%capture --no-stderr
%pip install --quiet -U langchain langchain_openai tavily-python
[notice] A new release of pip is available: 23.3.2 -> 24.0 [notice] To update, run: python3.11 -m pip install --upgrade pip
Next, we need to set API keys for OpenAI (the LLM we will use) and Tavily (the search tool we will use)
import os
import getpass
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = getpass.getpass("OpenAI API Key:")
os.environ["TAVILY_API_KEY"] = getpass.getpass("Tavily API Key:")
Optionally, we can set API key for LangSmith tracing, which will give us best-in-class observability.
os.environ["LANGCHAIN_TRACING_V2"] = "true"
os.environ["LANGCHAIN_API_KEY"] = getpass.getpass("LangSmith API Key:")
os.environ["LANGCHAIN_PROJECT"] = "Plan-and-execute"
from langchain_community.tools.tavily_search import TavilySearchResults
tools = [TavilySearchResults(max_results=3)]
Define our Execution Agent¶
Now we will create the execution agent we want to use to execute tasks. Note that for this example, we will be using the same execution agent for each task, but this doesn't HAVE to be the case.
from langchain import hub
from langchain.agents import create_openai_functions_agent
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
# Get the prompt to use - you can modify this!
prompt = hub.pull("hwchase17/openai-functions-agent")
# Choose the LLM that will drive the agent
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4-turbo-preview")
# Construct the OpenAI Functions agent
agent_runnable = create_openai_functions_agent(llm, tools, prompt)
from langgraph.prebuilt import create_agent_executor
agent_executor = create_agent_executor(agent_runnable, tools)
agent_executor.invoke(
{"input": "who is the winnner of the us open", "chat_history": []}
)
{'input': 'who is the winnner of the us open',
'chat_history': [],
'agent_outcome': AgentFinish(return_values={'output': 'The winners of the US Open in 2023 are as follows:\n\n- **Golf:** Wyndham Clark won the 2023 US Open in golf, holding his nerve against Rory McIlroy.\n \n- **Tennis:** The 2023 US Open tennis tournament details include information about the event and its prize money, but the winner has not been specified in the provided information. As of the last update, Carlos Alcaraz won the 2022 US Open tennis title.'}, log='The winners of the US Open in 2023 are as follows:\n\n- **Golf:** Wyndham Clark won the 2023 US Open in golf, holding his nerve against Rory McIlroy.\n \n- **Tennis:** The 2023 US Open tennis tournament details include information about the event and its prize money, but the winner has not been specified in the provided information. As of the last update, Carlos Alcaraz won the 2022 US Open tennis title.'),
'intermediate_steps': [(AgentActionMessageLog(tool='tavily_search_results_json', tool_input={'query': 'US Open winner 2023'}, log="\nInvoking: `tavily_search_results_json` with `{'query': 'US Open winner 2023'}`\n\n\n", message_log=[AIMessage(content='', additional_kwargs={'function_call': {'arguments': '{"query":"US Open winner 2023"}', 'name': 'tavily_search_results_json'}})]),
'[{\'url\': \'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/2023_U.S._Open_(golf)\', \'content\': \'Contents 2023 U.S. Open (golf) was selected to host the 123rd U.S. Open in June 2023. The USGA had made overtures to the club for at least 26 years. Final round[edit] Sunday, June 18, 2023 Third round[edit] Saturday, June 17, 2023Rory McIlroy falls short as Wyndham Clark holds nerve to win 2023 US Open. The Guardian. Archived from the original on June 19, 2023. Retrieved June 20, 2023.\'}, {\'url\': \'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/2023_US_Open_(tennis)\', \'content\': "The 2023 US Open is the 143rd consecutive edition of the tournament and will take place at the USTA Billie Jean King The total overall prize money for the 2023 US Open totals $65 million, 8% more than the 2022 edition.[4] Contents 2023 US Open (tennis) Wheelchair boys\' singles Dahnon Ward Wheelchair girls\' singles Ksénia Chasteau contract with ESPN, in which the broadcaster holds exclusive rights to the entire tournament and the US Open Series.Carlos Alcaraz defeats Casper Ruud for 2022 US Open title, world No. 1 ranking. US Open. Archived from the original on September 12, 2022. Retrieved September\\xa0..."}]')]}
Define the State¶
Let's now start by defining the state the track for this agent.
First, we will need to track the current plan. Let's represent that as a list of strings.
Next, we should track previously executed steps. Let's represent that as a list of tuples (these tuples will contain the step and then the result)
Finally, we need to have some state to represent the final response as well as the original input.
from langchain_core.pydantic_v1 import BaseModel, Field
from typing import List, Tuple, Annotated, TypedDict
import operator
class PlanExecute(TypedDict):
input: str
plan: List[str]
past_steps: Annotated[List[Tuple], operator.add]
response: str
Planning Step¶
Let's now think about creating the planning step. This will use function calling to create a plan.
from langchain_core.pydantic_v1 import BaseModel
class Plan(BaseModel):
"""Plan to follow in future"""
steps: List[str] = Field(
description="different steps to follow, should be in sorted order"
)
from langchain.chains.openai_functions import create_structured_output_runnable
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
planner_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(
"""For the given objective, come up with a simple step by step plan. \
This plan should involve individual tasks, that if executed correctly will yield the correct answer. Do not add any superfluous steps. \
The result of the final step should be the final answer. Make sure that each step has all the information needed - do not skip steps.
{objective}"""
)
planner = create_structured_output_runnable(
Plan, ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4-turbo-preview", temperature=0), planner_prompt
)
planner.invoke(
{"objective": "what is the hometown of the current Australia open winner?"}
)
Plan(steps=['Identify the current year.', 'Search for the Australia Open winner of the current year.', 'Find the hometown of the identified winner.'])
Re-Plan Step¶
Now, let's create a step that re-does the plan based on the result of the previous step.
from langchain.chains.openai_functions import create_openai_fn_runnable
class Response(BaseModel):
"""Response to user."""
response: str
replanner_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(
"""For the given objective, come up with a simple step by step plan. \
This plan should involve individual tasks, that if executed correctly will yield the correct answer. Do not add any superfluous steps. \
The result of the final step should be the final answer. Make sure that each step has all the information needed - do not skip steps.
Your objective was this:
{input}
Your original plan was this:
{plan}
You have currently done the follow steps:
{past_steps}
Update your plan accordingly. If no more steps are needed and you can return to the user, then respond with that. Otherwise, fill out the plan. Only add steps to the plan that still NEED to be done. Do not return previously done steps as part of the plan."""
)
replanner = create_openai_fn_runnable(
[Plan, Response],
ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4-turbo-preview", temperature=0),
replanner_prompt,
)
Create the Graph¶
We can now create the graph!
async def execute_step(state: PlanExecute):
task = state["plan"][0]
agent_response = await agent_executor.ainvoke({"input": task, "chat_history": []})
return {
"past_steps": (task, agent_response["agent_outcome"].return_values["output"])
}
async def plan_step(state: PlanExecute):
plan = await planner.ainvoke({"objective": state["input"]})
return {"plan": plan.steps}
async def replan_step(state: PlanExecute):
output = await replanner.ainvoke(state)
if isinstance(output, Response):
return {"response": output.response}
else:
return {"plan": output.steps}
def should_end(state: PlanExecute):
if "response" in state and state["response"]:
return "True"
else:
return "False"
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, END
workflow = StateGraph(PlanExecute)
# Add the plan node
workflow.add_node("planner", plan_step)
# Add the execution step
workflow.add_node("agent", execute_step)
# Add a replan node
workflow.add_node("replan", replan_step)
workflow.set_entry_point("planner")
# From plan we go to agent
workflow.add_edge("planner", "agent")
# From agent, we replan
workflow.add_edge("agent", "replan")
workflow.add_conditional_edges(
"replan",
# Next, we pass in the function that will determine which node is called next.
should_end,
{
# If `tools`, then we call the tool node.
"True": END,
"False": "agent",
},
)
# Finally, we compile it!
# This compiles it into a LangChain Runnable,
# meaning you can use it as you would any other runnable
app = workflow.compile()
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage
config = {"recursion_limit": 50}
inputs = {"input": "what is the hometown of the 2024 Australia open winner?"}
async for event in app.astream(inputs, config=config):
for k, v in event.items():
if k != "__end__":
print(v)
{'plan': ['Wait until the 2024 Australian Open concludes.', 'Identify the winner of the 2024 Australian Open.', "Research the winner's biography to find their hometown.", 'The hometown of the 2024 Australian Open winner is the result found in the previous step.']}
{'past_steps': ('Wait until the 2024 Australian Open concludes.', "I can't wait for real-time events. However, I can help you find out the schedule, expected dates, or any other information regarding the 2024 Australian Open. How can I assist you further?")}
{'plan': ['Identify the winner of the 2024 Australian Open.', "Research the winner's biography to find their hometown.", 'The hometown of the 2024 Australian Open winner is the result found in the previous step.']}
{'past_steps': ('Identify the winner of the 2024 Australian Open.', "The winners of the 2024 Australian Open were Jannik Sinner in the men's singles and Aryna Sabalenka in the women's singles. Jannik Sinner defeated Daniil Medvedev in the final, while specific details about Aryna Sabalenka's match are not provided in the information retrieved.")}
{'plan': ["Research Jannik Sinner's biography to find his hometown.", "Research Aryna Sabalenka's biography to find her hometown.", 'The hometowns of the 2024 Australian Open winners are the results found in the previous steps.']}
{'past_steps': ("Research Jannik Sinner's biography to find his hometown.", 'Jannik Sinner was born in San Candido (Innichen), Italy, on August 16, 2001. This is considered his hometown.')}
{'plan': ["Research Aryna Sabalenka's biography to find her hometown.", 'The hometowns of the 2024 Australian Open winners are the results found in the previous steps.']}
{'past_steps': ("Research Aryna Sabalenka's biography to find her hometown.", 'Aryna Sabalenka was born in Minsk, the capital of Belarus.')}
{'response': 'The hometowns of the 2024 Australian Open winners are San Candido (Innichen), Italy for Jannik Sinner, and Minsk, Belarus for Aryna Sabalenka. No further steps are needed as the final answer has been reached.'}
Conclusion¶
Congrats on making a plan-and-execute agent! One known limitations of the above design is that each task is still executed in sequence, meaning embarrassingly parallel operations all add to the total execution time. You could improve on this by having each task represented as a DAG (similar to LLMCompiler), rather than a regular list.